Note
Click here to download the full example code
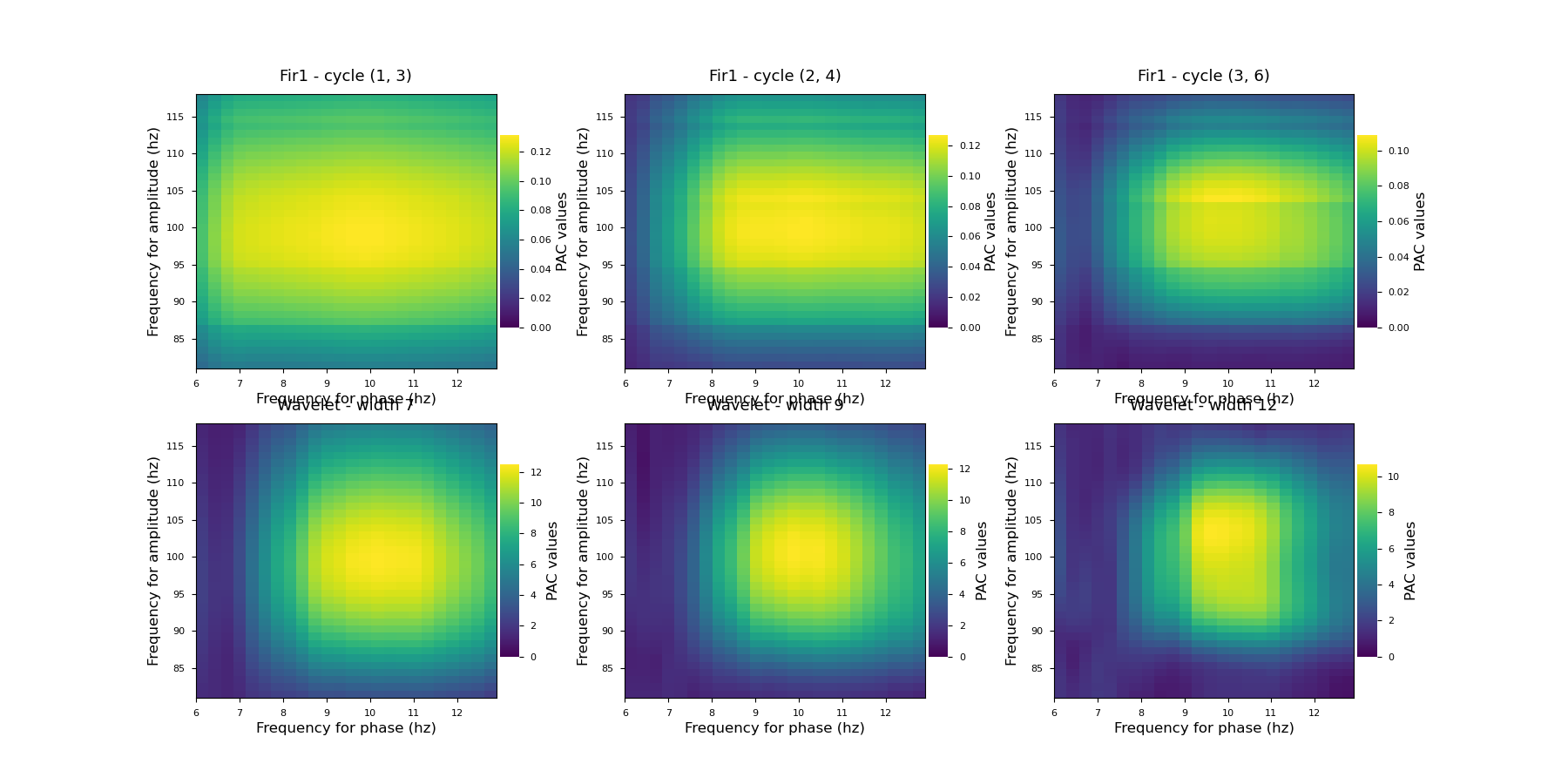
Compare filtering properties¶
Tensorpac provides two ways for extracting phase and amplitude :
Using filtering followed by Hilbert transform.
Using wavelets.
Out:
Filtering with fir1 filter
Filtering with wavelets
from __future__ import print_function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorpac import Pac
from tensorpac.signals import pac_signals_wavelet
plt.style.use('seaborn-paper')
# First, we generate a dataset of signals artificially coupled between 10hz
# and 100hz. By default, this dataset is organized as (ntrials, n_times) where
# n_times is the number of time points.
n_epochs = 5 # number of datasets
n_times = 4000 # number of time points
data, time = pac_signals_wavelet(f_pha=10, f_amp=100, noise=1.,
n_epochs=n_epochs, n_times=n_times)
# First, let's use the MVL, without any further correction by surrogates :
p = Pac(idpac=(1, 0, 0), f_pha=(5, 14, 2, .3), f_amp=(80, 120, 2, 1),
verbose=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 9))
# Define several cycle options for the fir1 (eegfilt like) filter :
print('Filtering with fir1 filter')
for i, k in enumerate([(1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 6)]):
p.cycle = k
xpac = p.filterfit(1024, data, n_jobs=1)
plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1)
p.comodulogram(xpac.mean(-1), title='Fir1 - cycle ' + str(k))
# Define several wavelet width :
p.dcomplex = 'wavelet'
print('Filtering with wavelets')
for i, k in enumerate([7, 9, 12]):
p.width = k
xpac = p.filterfit(1024, data)
plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 4)
p.comodulogram(xpac.mean(-1), title='Wavelet - width ' + str(k))
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.322 seconds)
